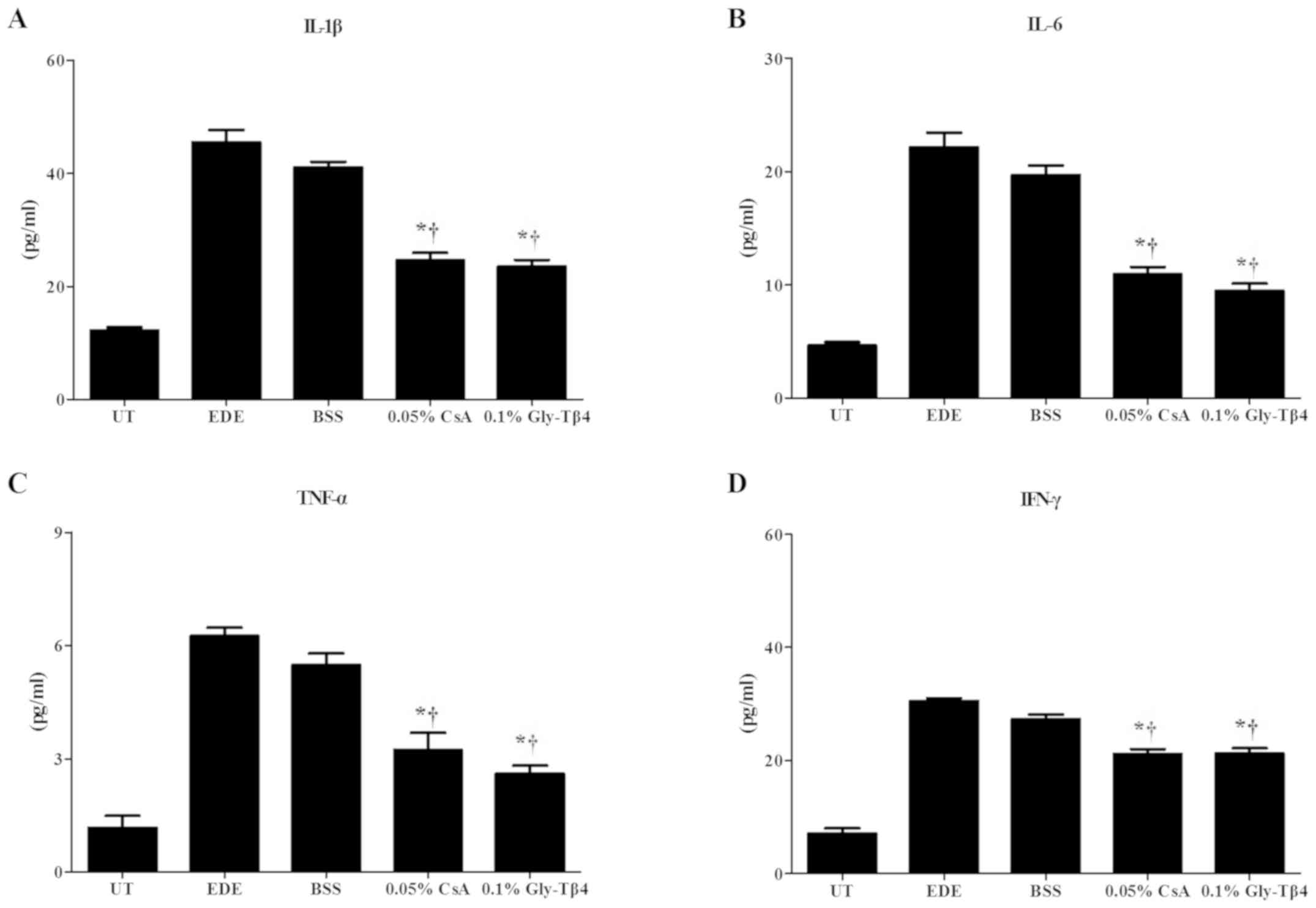
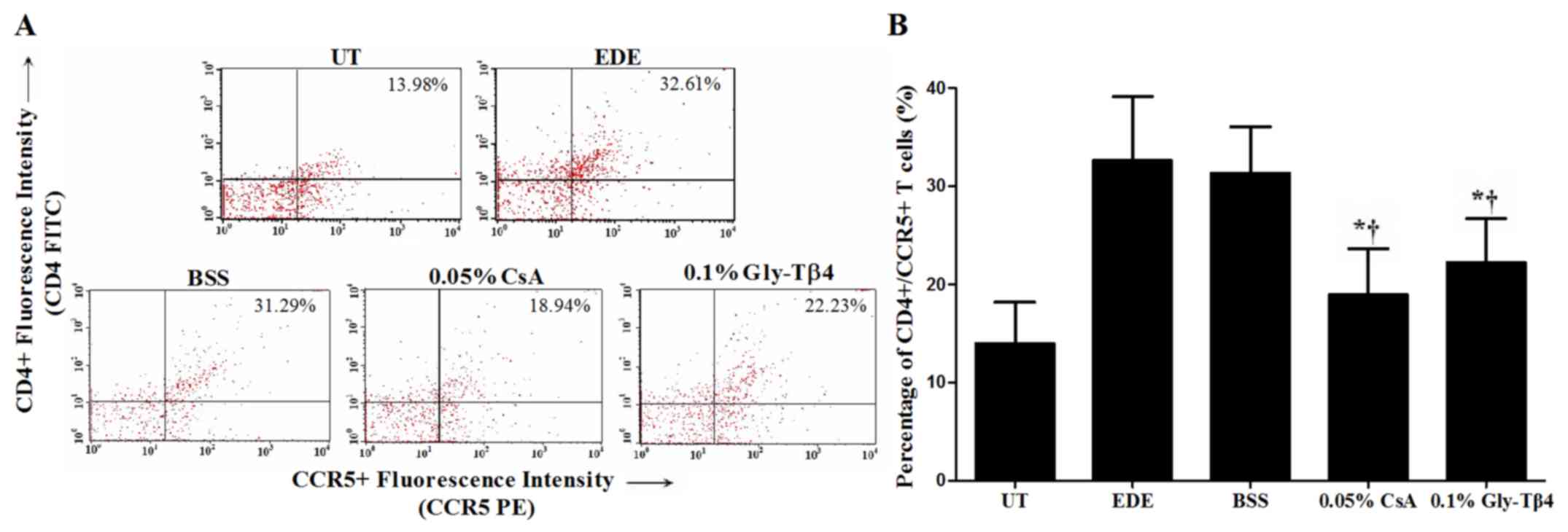
|
1
|
The epidemiology of dry eye disease:
Report of the epidemiology subcommittee of the international dry
eye workshop (2007). Ocul Surf 5: 93-107, 2007.
|
|
2
|
Farrand KF, Fridman M, Stillman IÖ and
Stillman IO: Prevalence of diagnosed dry eye disease in the united
states among adults aged 18 years and older. Am J Ophthalmol.
182:90–98. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Wolffsohn JS, Arita R, Chalmers R,
Djalilian A, Dogru M, Dumbleton K, Gupta PK, Karpecki P, Lazreg S,
Pult H, et al: TFOS DEWS II diagnostic methodology report. Ocul
Surf. 15:539–574. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Yoon KC, De Paiva CS, Qi H, Chen Z, Farley
WJ, Li DQ and Pflugfelder SC: Expression of Th-1 chemokines and
chemokine receptors on the ocular surface of C57BL/6 mice: Effects
of desiccating stress. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 48:2561–2569.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Craig JP, Nichols KK, Akpek EK, Caffery B,
Dua HS, Joo CK, Liu Z, Nelson JD, Nichols JJ, Tsubota K and
Stapleton F: TFOS DEWS II definition and classification report.
Ocul Surf. 15:276–283. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Stern ME and Pflugfelder SC: Inflammation
in dry eye. Ocul Surf. 2:124–130. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Pflugfelder SC, De Paiva CS, Li DQ and
Stem ME: Epithelial-immune cell interaction in dry eye. Cornea.
27:S9–S11. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Bucolo C, Musumeci N, Musumeci S and Drago
F: Acidic mammalian chitinase and the eye: Implications for ocular
inflammatory diseases. Front Pharmacol. 2(43)2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Bucolo C, Fidilio A, Fresta CG, Lazzara F,
Platania CBM, Cantarella G, Di Benedetto G, Burgaletto C,
Bernardini R, Pizza C, et al: Ocular pharmacological profle of
hydrocortisone in dry eye disease. Front Pharmacol.
10(1240)2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Li Y, Cui L, Lee HS, Kang YS, Choi W and
Yoon KC: Comparison of 0.3% hypotonic and isotonic sodium
hyaluronate eye drops in the treatment of experimental dry eye.
Curr Eye Res. 42:1108–1114. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Yang JM, Choi W, Kim N and Yoon KC:
Comparison of topical cyclosporine and diquafosol treatment in dry
eye. Optom Vis Sci. 92:e296–e302. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Kim HS, Kim TI, Kim JH, Yoon KC, Hyon JY,
Shin KU and Choi CY: Evaluation of clinical efficacy and safety of
a novel cyclosporine A nanoemulsion in the treatment of dry eye
syndrome. J Ocul Phamacol Ther. 33:530–538. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
De Oliveira and Wilson SE: Practical
guidance for the use of cyclosporine ophthalmicsolutions in the
management of dry eye disease. Clin Ophthalmol. 13:1115–1122.
2019.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Crockford D, Turjman N, Allan C and Angel
J: Thymosin beta4: Structure, function, and biological properties
supporting current and future clinical applications. Ann NY Acad
Sci. 1194:179–189. 2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Huff T, Müller CS, Otto AM, Netzker R and
Hannappel E: beta-Thymosins, small acidic peptides with multiple
functions. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 33:205–220. 2001.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Sosne G, Qiu P, Christopherson PL and
Wheater MK: Thymosin beta 4 suppression of corneal NFkappaB: A
potential anti-inflammatory pathway. Exp Eye Res. 84:663–669.
2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Pardon MC: Anti-inflammatory potential of
thymosin β4 in the central nervous system: Implications for
progressive neurodegenerative diseases. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 18
(Suppl 1):S165–S169. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sosne G and Ousler GW: Thymosin beta 4
ophthalmic solution for dry eye: A randomized, placebo-controlled,
phase II clinical trial conducted using the controlled adverse
environment (CAE™) model. Clin Ophthalmol. 9:877–884.
2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sosne G, Dunn SP and Kim C: Thymosin β4
significantly improves signs and symptoms of severe dry eye in a
phase 2 randomized trial. Cornea. 34:491–496. 2015.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang W, Nie L, Du L, Chen W, Wu Z and Jin
Y: Topical treatment of corneal alkali burns with Gly-thymosin
β4 solutions and in situ hydrogels via inhibiting
corneal neovascularization and improving corneal epidermal recovery
in experimental rabbits. Burns. 43:1742–1747. 2017.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Yoon KC, De Paiva CS, Qi H, Chen Z, Farley
WJ, Li DQ, Sterm ME and Pflugfelder SC: Desiccating environmental
stress exacerbates autoimmune lacrimal keratoconjunctivitis in
non-obese diabetic mice. J Autoimmun. 30:212–221. 2008.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yoon KC, Ahn KY, Choi W, Li Z, Choi JS,
Lee SH and Park SH: Tear production and ocular surface changes in
experimental dry eye after elimination of desiccating stress.
Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 52:7267–7273. 2011.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Villareal AL, Farley W and Pflugfelder SC:
Effect of topical ophthalmic epinastine and olopatadine on tear
volume in mice. Eye Contact Lens. 32:272–276. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Pauly A, Brignole-Baudouin F, Labbė A,
Liang H, Warnet JM and Baudouin C: New tools for the evaluation of
toxic ocular surface changes in the rat. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci.
48:5473–5483. 2007.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yoon KC, Park CS, You IC, Choi HJ, Lee KH,
Im SK, Park HY and Pflugfelder SC: Expression of CXCL9, -10, -11,
and CXCR3 in the tear film and ocular surface of patients with dry
eye syndrome. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 51:643–650.
2010.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Shah R, Reyes-Gordillo K, Cheng Y,
Varatharajalu R, lbrahin J and Lakshman MR: Thymosin β4 prevents
oxidative stress, inflammation, and fibrosis in ethanol- and
LPS-induced liver injury in mice. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2018(9630175)2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Cacasin MA: Therapeutic potential of
thymosin-beta4 and its derivative
N-acetyl-seryl-aspartyl-lysyl-proline (Ac-SDKP) in cardiac healing
after infarction. Am J Cardiovasc Drugs. 6:305–311. 2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Goldstein AL, Hannappel E, Sosne G and
Kleinman HK: Thymosin β4: A multi-functional regenerative peptide.
Basic properties and clinical applications. Expert Opin Biol Ther.
12:37–51. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Gulati A, Sacchetti M, Bonini S and Dana
R: Chemokine receptor CCR5 expression in conjunctival epithelium of
patients with dry eye syndrome. Arch Ophthalmol. 124:710–716.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
EI Annan J, Chauhan SK, Ecoiffier T, Zhang
Q, Saban DR and Dana R: Characterization of effector T cells in dry
eye disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 50:3802–3807.
2009.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Li Y, Jin R, Li L, Hsu HH, You IC, Yoon HJ
and Yoon KC: Therapeutic effect of topical adiponectin-derived
short peptides compared with globular adiponectin in experimental
dry eye and alkali burn. J Ocul Phamacol Ther. 36:88–96.
2020.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Choi W, Li Z, Oh HJ, Im SK, Lee SH, Park
SH, You IC and Yoon KC: Expression of CCR5 and its ligands CCL3,
-4, and -5 in the tear film and ocular surface of patients with dry
eye disease. Curr Eye Res. 37:12–17. 2012.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Boboridis KG and Konstas AGP: Evaluating
the novel application of cyclosporine 0.1% in ocular surface
disease. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 19:1027–1039. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Yin J, Kheirkhah A, Dohiman T, Saboo U and
Dana R: Reduced efficacy of low-dose topical steroids in dry eye
disease associated with graft-versus-host disease. Am J Ophthalmol.
190:17–23. 2018.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Pflugfelder SC: Integrating restasis into
the management of dry eye. Int Ophthlamol Clin. 46:101–103.
2006.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Sosne G, Xu L, Prach L, Mrock LK, Kleinman
HK, Letterio JJ, Hazlett LD and Kurpakus-Wheater M: Thymosin beta 4
stimulates laminin-5 production independent of TGF-beta. Exp Cel
Res. 293:175–183. 2004.PubMed/NCBI View Article : Google Scholar
|